RENEWABLE ENERGIES IN SPAIN
Discovering Spain's renewable energy potential
In the face of the growing global energy demand and the urgent need to address climate change, renewable energies have become the essential pillar of the energy sector in Spain.
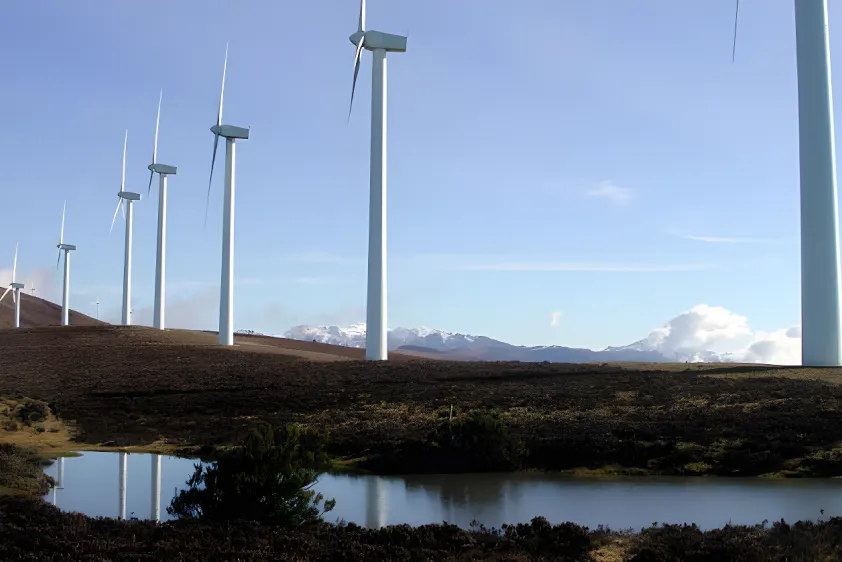

Elgea-Urkilla wind farm in the Basque Country.
The transition towards a more sustainable energy model involves using renewable energies. These play a crucial role, as they have the potential to reduce CO2 emissions associated with energy generation by up to 90%.
At Iberdrola España, we have been leading the energy revolution for more than two decades with our commitment to renewable energies. Our vision is based on building a green and clean energy model that guarantees a sustainable future for generations to come, using energy from natural sources.
What are renewable energies?
Renewable energies are energy sources that come from inexhaustible natural resources, either because they contain a large amount of energy, such as sun and wind, or because they are capable of regenerating themselves in a short period of time – without generating greenhouse gas emissions.
Thanks to technological advances, the production and maintenance costs of renewable energy infrastructures have fallen considerably, making these forms of energy increasingly accessible and competitive
History of renewable energies in Spain
The history of renewable energies in Spain dates back to the end of the 19th century, when hydroelectric power began to be used to generate electricity. However, it was not until the end of the 20th century that a more significant interest in renewable energies began, due to the global energy crisis and the growing awareness of the need to diversify the energy matrix.
During the 1980s and 1990s, Spain experienced a gradual growth in the development and use of hydroelectric power and wind energy, with the construction of numerous wind farms and hydroelectric plants throughout the country. Our pioneering commitment to renewables led us to build the first grid-connected photovoltaic installation in Spain – the 100 KW pilot plant in San Agustín de Guadalix in 1984.
However, the renewables boom intensified with the implementation of various plans for promoting renewable energies at the beginning of the 21st century, to increase renewables installed capacity in Spain and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
In recent years, Spain has set itself the goal of achieving decarbonisation of its energy model by 2050. To achieve this goal, increases in renewable generation capacity of at least 3 GW per year are planned for the coming decades.
Main renewable energies in Spain
Among the main renewable energies in Spain, we highlight the following:
-
Wind energy. Wind energy comes from wind. Wind farms, consisting of large wind turbines, capture the kinetic energy of the wind and convert it into electricity. Wind energy is inexhaustible, renewable and clean, which reduces CO2 and other greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Hydroelectric energy. Hydropower is produced by the movement of water, whether by currents, waterfalls or tides. It harnesses the mechanical energy of moving water to transform it into electricity through hydroelectric power plants. Like other renewable energies, hydropower is clean and inexhaustible.
-
Solar energy. Solar energy is a renewable and clean source of energy that uses solar radiation to produce electricity from the photoelectric effect. Electricity is obtained by installing photovoltaic panels. More and more people are opting for photovoltaic self-consumption in Spain, both households and businesses.
Benefits of renewable energies
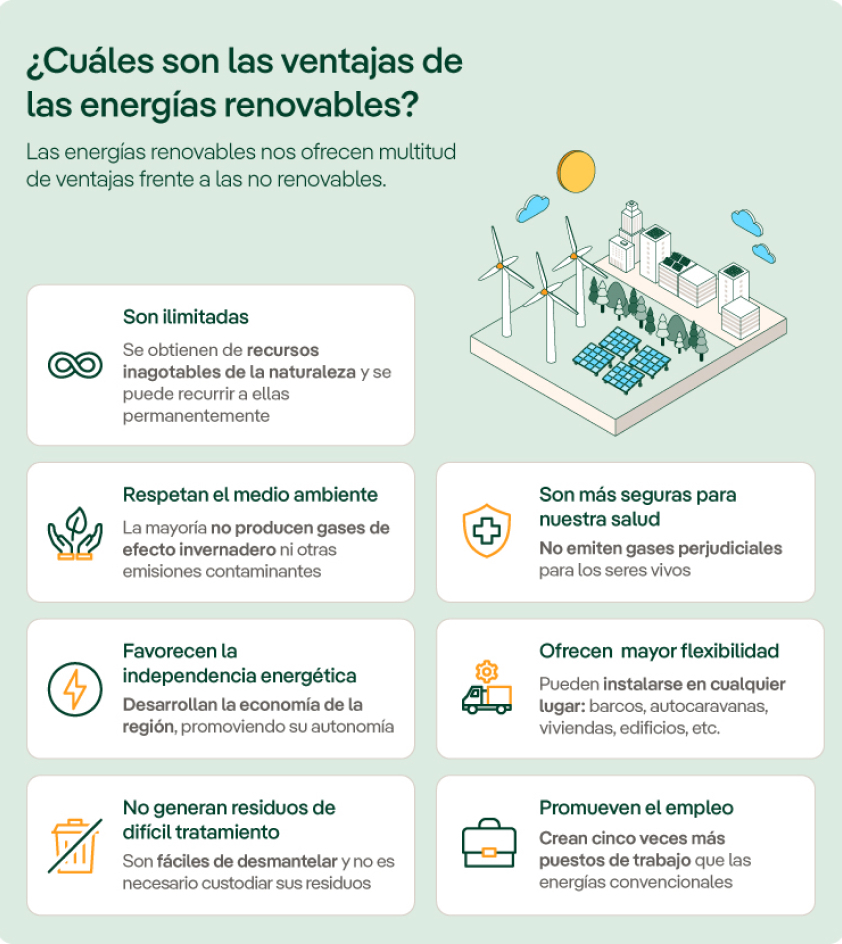
Differences between renewable and non-renewable energies
The main distinction between renewable and non-renewable energies lies in their long-term energy production capacity. Renewable energies come from sources that are constantly regenerating or non-depleting, ensuring infinite energy production; whereas non-renewable energies depend on finite reserves that are depleting with use or regenerating very slowly.
Moreover, renewable energies are highly sustainable and have a considerably smaller environmental footprint than non-renewable energies.
Leading Spanish regions for renewable energy industry
According to Red Eléctrica's published report on renewable energies in the Spanish electricity system, renewables reached a historic milestone in 2023, representing 50.3% of national electricity generation. This represents an increase of 8.1 percentage points over the previous year, when renewable energies contributed 42.2 % to the national energy mix.
However, the distribution varies significantly between regions. As the study reports, most of the installed renewable capacity is located in Castilla y León, Castilla-La Mancha, Andalusia and Extremadura, which together account for almost 60% of the installed renewable capacity of the national electricity system.
Castilla y León leads as the autonomous community with the largest installed renewable energy capacity in Spain, with a total of 13,046 MW. It is followed by Castilla-La Mancha in second place, with an installed capacity of 12,120 MW. In third place is Andalusia, with an installed renewable energy capacity of 11,100 MW.
Spain’s renewable energy in figures
Main renewable energies in Spain
According to data from Red Eléctrica, Spain ranks second in Europe in installed renewable capacity and in wind and solar generation. Wind energy remains the most prominent renewable technology in the national energy landscape. In 2023, it reached an all-time record, accounting for 23.5% of total energy output – an increase of 1.3 percentage points compared to the previous year. In Spain, wind energy is followed by solar photovoltaic energy (20.3%) in second place; and hydroelectric energy (13.6%), in third place.
How Iberdrola España is contributing to renewable energy
Iberdrola España, with more than a century of history, has positioned itself as a leader in renewable energy within the Spanish energy sector. Thanks to our diversified business portfolio, we installed 22,620 MW of renewable energy capacity in Spain at the end of the first quarter of 2025. This commitment is part of our drive to lead the energy transition in the country, thus strengthening our commitment to building a cleaner and more sustainable future.
Principales energías renovables en Iberdrola España
CONVIVE programme, the key to promoting sustainable development in renewable energies
One of the solutions that Iberdrola España has developed to promote socioeconomic development and the preservation of biodiversity was through its Convive Programme. This initiative was born to be a continuous improvement programme that integrates all initiatives and alliances aimed at promoting coexistence between renewable energies promoted by Iberdrola España.
The programme has three main areas of focus:
- Boosting socio-economic development by implementing initiatives that foster economic and social development at the local and national level.
- Protecting and enhancing biodiversity through actions that integrate facilities into the territory and landscape, improving their contribution to biodiversity and minimising their environmental impact.
- Learning from experts: improving the impact of renewables and social acceptance of the energy transition through collaboration with experts.













