STORAGE BATTERIES IN SPAIN
Storage batteries in Spain, the pathway to a greener and more sustainable economy
Electricity is a resource easy to generate, transport and transform, but its storage is a constant challenge in today's energy landscape. In order to make the production of renewable energy more flexible and ensure its integration into the system, storage solutions have been developed. This avoids wasting energy in times of low demand. Among the different storage systems, batteries stand out.
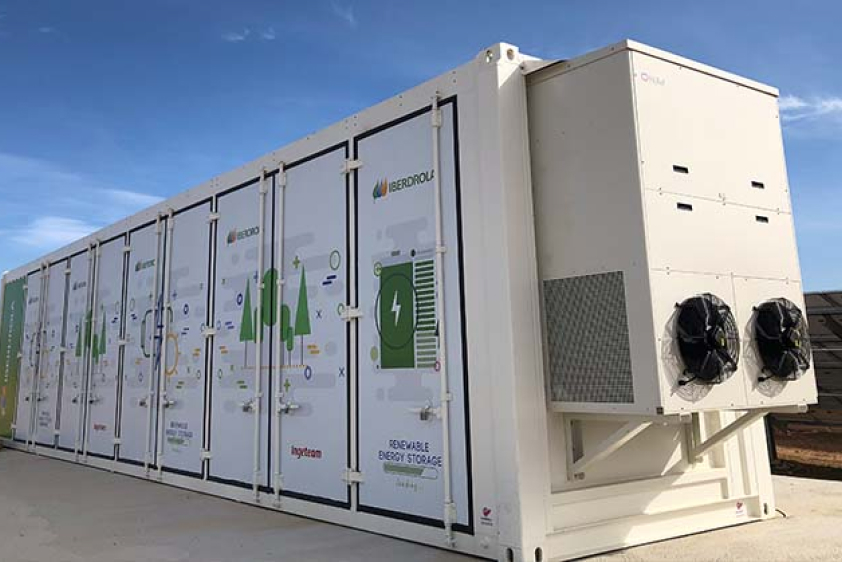

Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) are one of the latest solutions for storing energy for later use. The batteries have a mechanism that allows energy to flow in both directions to charge and discharge the batteries. In this way, the battery is charged at times when there is overproduction and supplies energy when there is a peak demand for electricity, allowing the surplus energy to be managed.
This technology has a variety of types, each with its own distinctive features. Among their benefits are the capacity for back-up during periods of energy demand, millisecond grid frequency regulation and optimisation of the integration of renewables into the system. Their speed of response, ease of installation and scalability make them efficient energy solutions.
Types of batteries in the Spanish energy sector
From modern lithium-ion batteries to sodium-ion batteries, at Iberdrola España we are implementing initiatives of different sizes in order to meet the energy needs in projects in Spain.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
In the search for solutions for the storage of energy generated by renewable sources, lithium-ion batteries are currently the most widespread solutions given their performance, technological maturity and cost ratio. These systems can be used stand-alone or in conjunction with renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind energy.
Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable and use lithium compounds as one of their electrodes. They were developed by Akira Yoshino in 1985, based on earlier research by John Goodenough and other experts. Six years later, Sony launched the first commercial version. Over time, improvements were introduced, such as the use of nickel-manganese-cobalt oxide (NMC) cathodes, which increased charge density, performance and safety.
Thanks to the high electrochemical potential of lithium – one of the smallest elements in the periodic table –, these batteries are able to store more energy in less space than other batteries. In addition to being lightweight and efficient, their cost has fallen by 85% since 2010 and is expected to continue to fall over the next decade.
Sodium-ion batteries
With the will to explore alternative raw materials to the use of lithium for the manufacture of energy storage resources, sodium-ion batteries have emerged. Sodium-ion batteries have emerged as an optimal option due to the relative abundance of this mineral and its low cost.
Sodium-ion batteries use sodium ions (Na+) instead of lithium ions (Li+). Sodium, abundant in nature, is an alkaline metal found in sea salt and the earth's crust. Although they have been studied since the 1980s, their potential for energy storage was rediscovered in the 21st century.
According to BloombergNEF, sodium-ion batteries are expected to account for 23% of the stationary storage market by 2030 – exceeding 50 GWh, with the potential to grow further through technological advances and efficient manufacturing.
Innovation and the future of batteries at Iberdrola
BESSs are an innovative solution for renewable energy storage, which is becoming increasingly important as demand for clean energy rises. They can improve the quality of supply, ensure grid stability and integrate renewable energy.
At Iberdrola España, we combine the use of batteries with wind energy and photovoltaic renewable energy projects (hybridisation). Examples of this are the facilities located at the Arañuelo photovoltaic plant or the Urkilla wind farm.
Energy Storage Innovation Projects
At Iberdrola España, we have a clear commitment to the development of innovative projects in energy storage. In this way, we maximise the use of energy and continue to promote the efficient integration of renewable energies into the electricity grid. Below, we highlight the innovative energy storage projects developed by the company.

Santiago Jares
Valdecañas
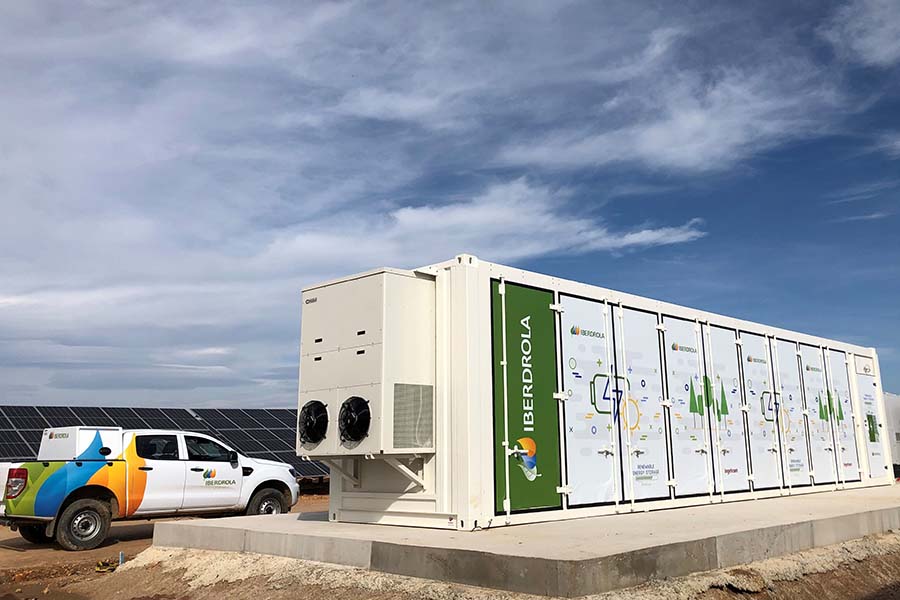


Campo Arañuelo III
Abadiño


Urkilla
Green hydrogen plant at Puertollano


Valcarlos
PERTE-supported facilities

Emerging trends in Spain and their impact
According to a recent BloombergNEF (BNEF) study, lithium-ion battery costs are expected to decline significantly in the coming years – surpassing even the 85% reduction experienced between 2010 and 2018. In this regard, BNEF projects a 50% reduction in costs per kW/h by 2030, driven by growing demand in two key markets: stationary storage and electric vehicles.
This forecast anticipates an exponential increase in global energy storage installations from a modest 9GW/17GWh in 2018 to 1,095GW/2,850GWh by 2040, requiring an investment of approximately $662 billion.
According to BNEF, the total battery demand for the stationary storage and electric transport sectors will reach 4,584 GWh by 2040. This increase not only drives the energy transition, but also creates a significant opportunity for battery manufacturers and companies involved in the extraction of key components, such as lithium, cobalt and nickel.